CAXA工艺图表2025
软件详情
CAXA 工艺图表 2025 是一款集 CAD 与 CAPP 于一体的工艺编制软件。它拥有 Office+CAD 双重能力,既能像办公软件一样处理文字,又能像 CAD 软件一样绘制和编辑图形
强大的绘图与图形处理能力:包含 CAXA 电子图板 CAD 2025 所有功能,可直接绘制图形,也能插入 dwg、dxf、exb 等格式图形并进行编辑。支持工序简图的参数化驱动,简图大小可根据输入的尺寸参数动态变化。
丰富的工艺知识库:提供各种行业工艺卡片模板及常用工艺知识信息,方便企业沉淀和重用典型工艺知识。用户还可根据需要扩充工艺知识库。
软件下载 https://pan.quark.cn/s/4892d393038d
安装前关闭杀毒软件
安装步骤
01解压安装包
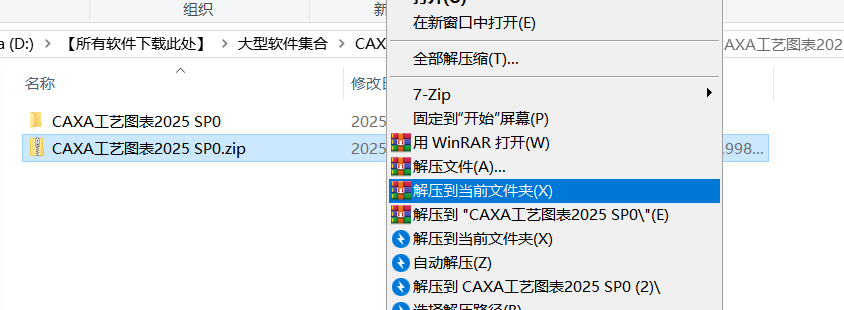
02右键Setup.exe以管理员运行
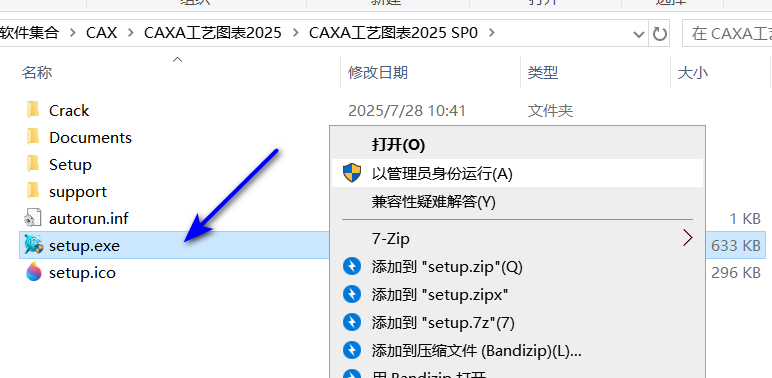
03电脑是多少位就选哪个
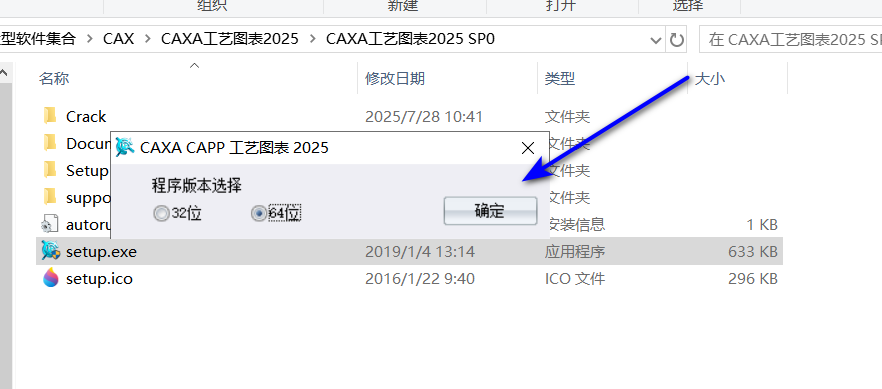
04下一步

05更改安装位置,根据自己需要选择安装的组件

06等待安装
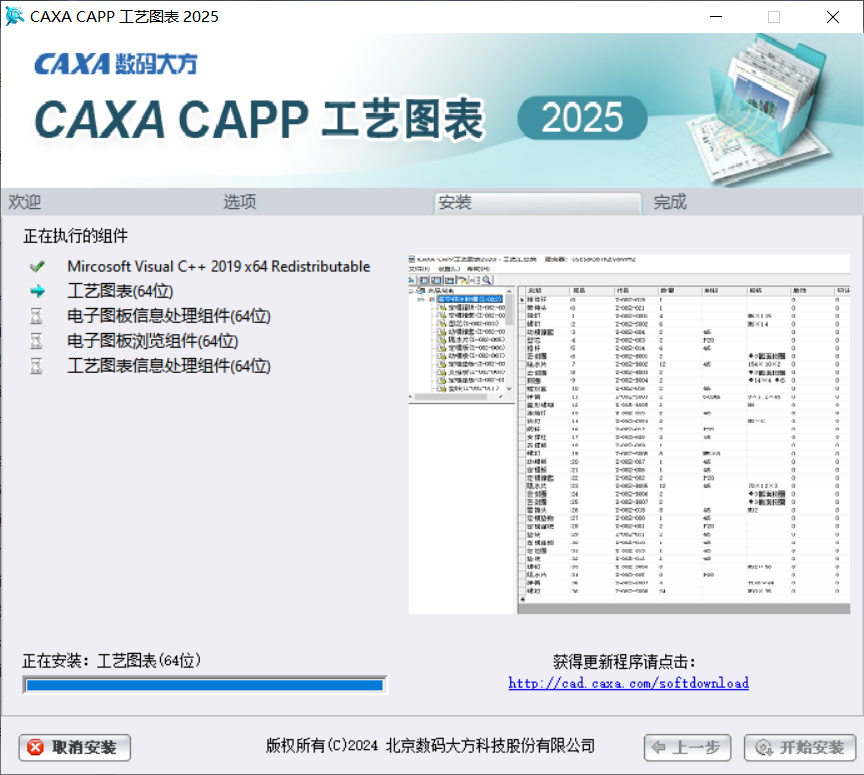
07安装完成
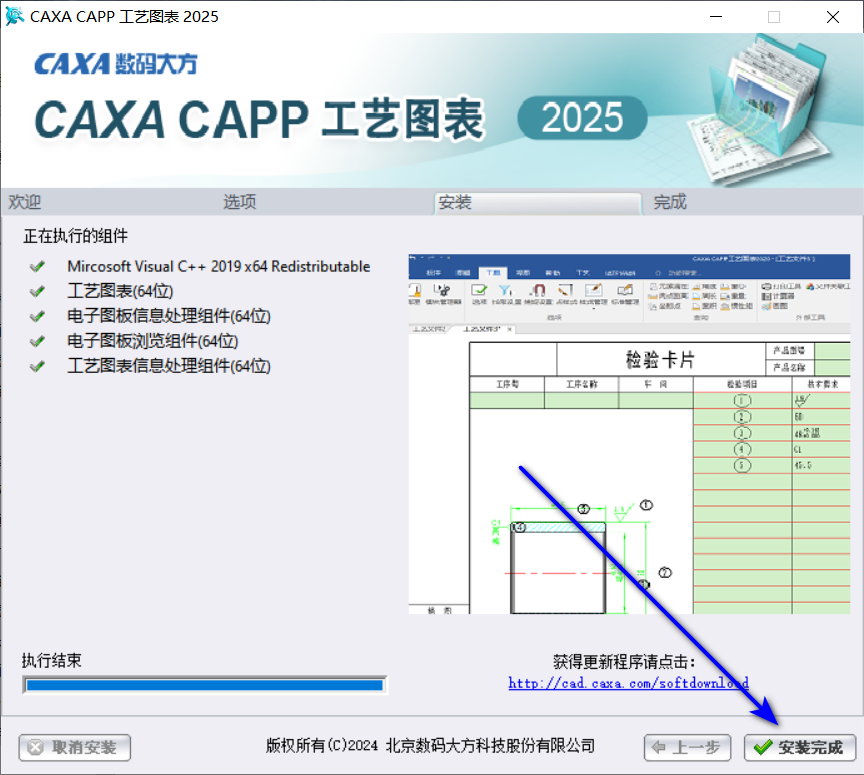
08点击安装完成
09打开Crack文件夹
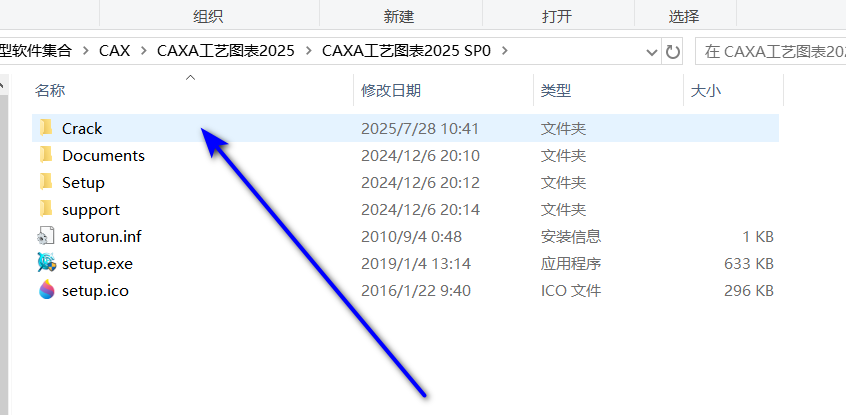
10右键Keygen以管理员运行

11选择工业2025点击GO

12点击是
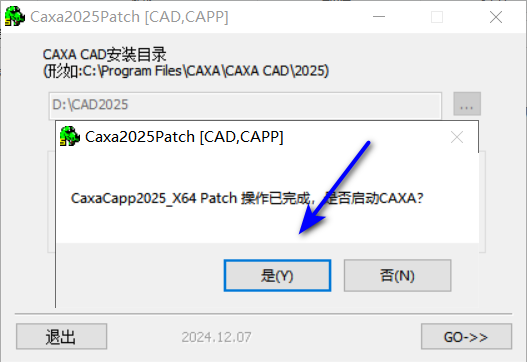
13安装完毕

